| Western blot (WB): | 1:500-2000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC): | 1:50-400 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF): | 1:50-400 |
| Flow Cytometry (Fixed): | 1:50-200 |
| Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): | 1:100-1000 |
| (Boiling the paraffin sections in 10mM citrate buffer,pH6.0,or PH8.0 EDTA repair liquid for 20 mins is required for the staining of formalin/paraffin sections.) Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user. | |
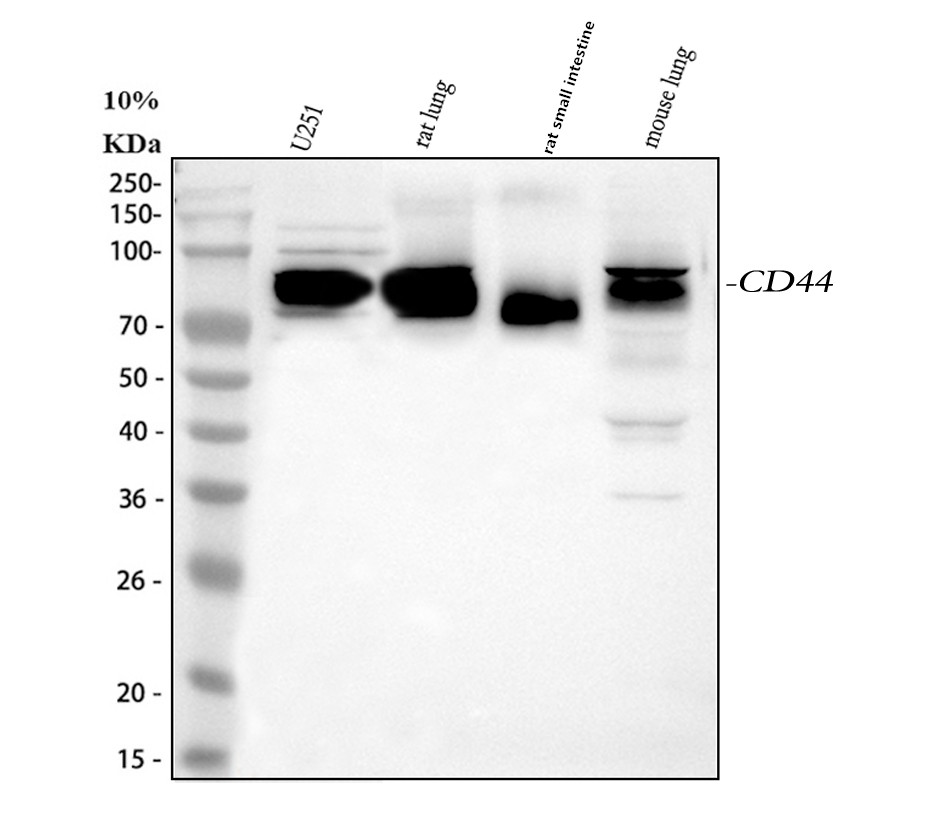
Figure 1. Western blot analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052). The sample well of each lane was loaded with 30 ug of sample under reducing conditions.
Lane 1: human U251 whole cell lysates,
Lane 2: rat lung tissue lysates,
Lane 3: rat small intestine tissue lysates,
Lane 4: mouse lung tissue lysates.
After electrophoresis, proteins were transferred to a membrane. Then the membrane was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 antigen affinity purified polyclonal antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:1000 and probed with a goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP secondary antibody (Catalog # BA1054). The signal is developed using ECL Plus Western Blotting Substrate (Catalog # AR1197). A specific band was detected for CD44 at approximately 82 kDa. The expected band size for CD44 is at 82 kDa.
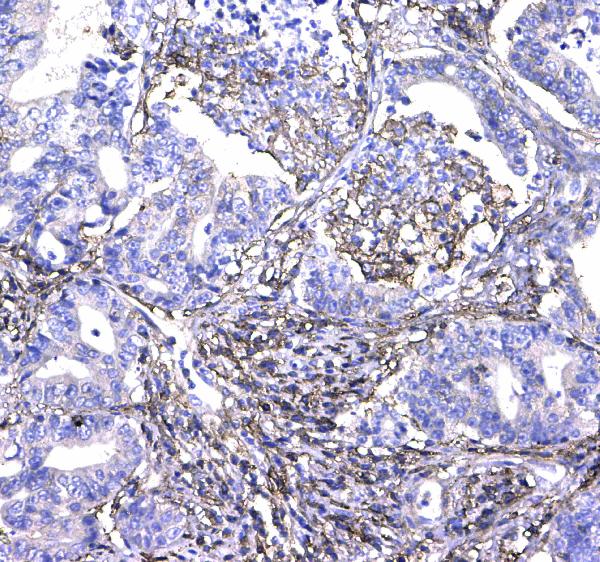
Figure 2. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of human colon cancer tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.
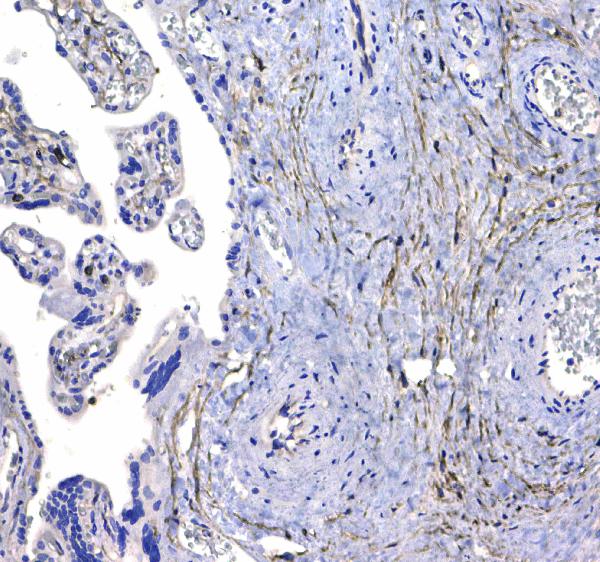
Figure 3. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of human placenta tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.
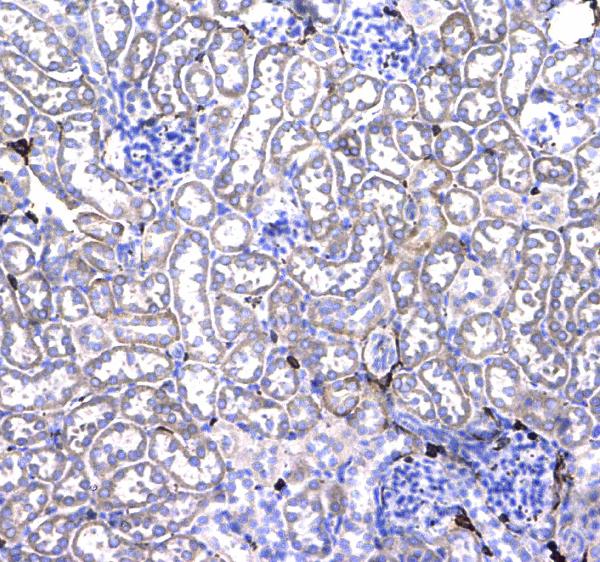
Figure 4. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of mouse kidney tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.
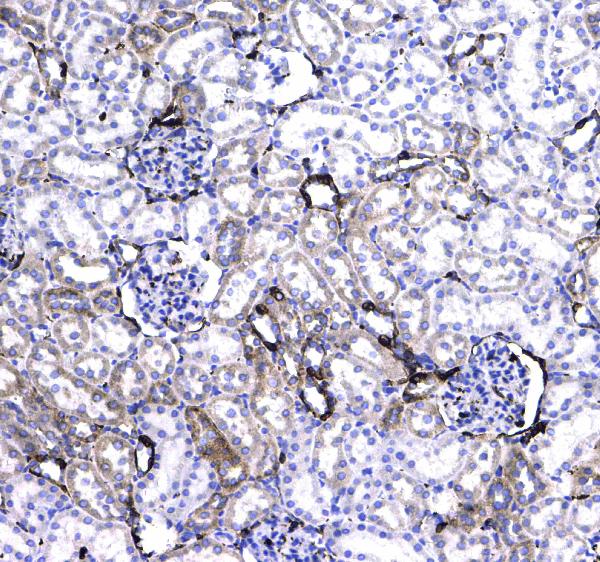
Figure 5. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of rat kidney tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.
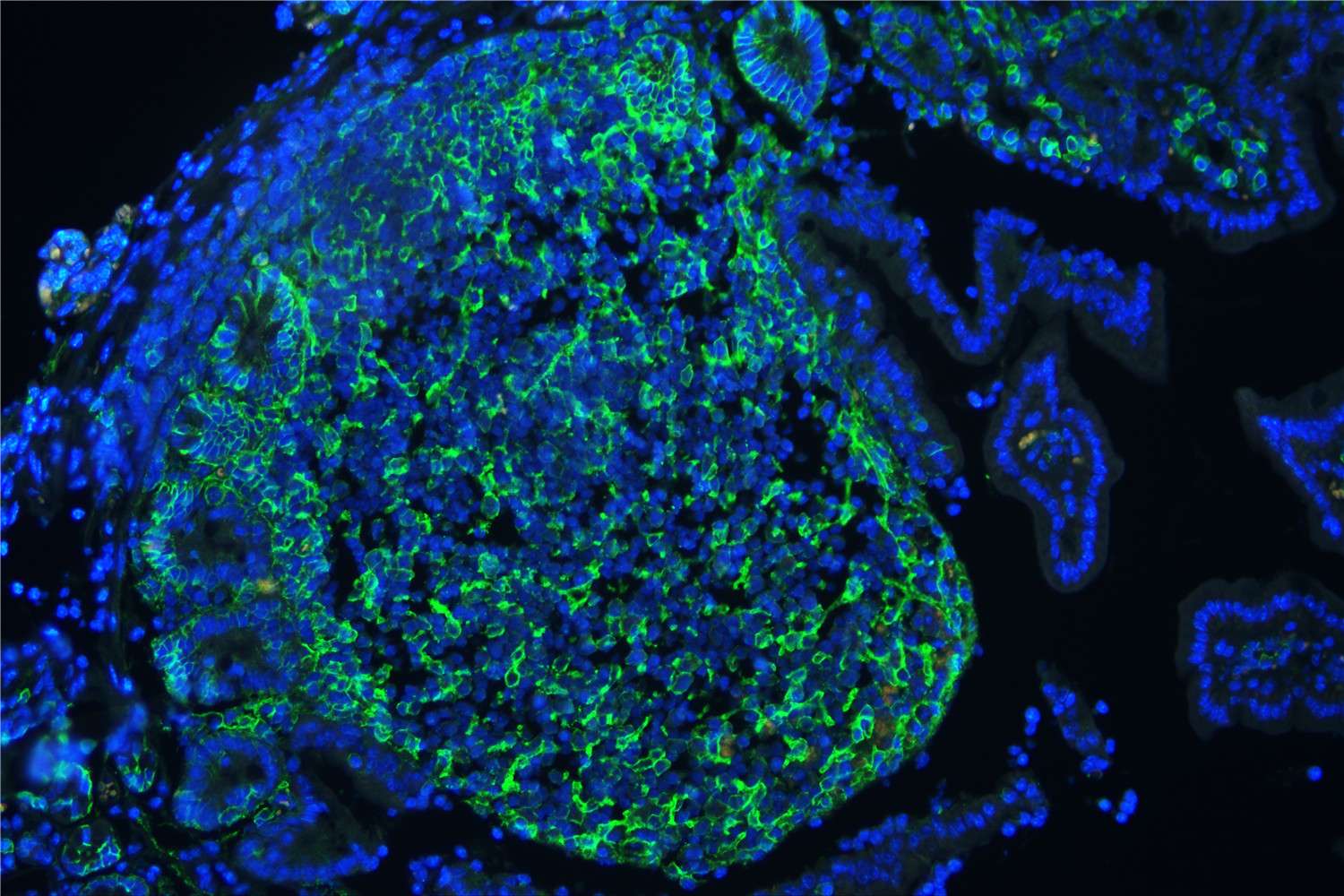
Figure 6. IF analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052)CD44 was detected in paraffin-embedded section of mouse lymphaden tissues. Heat mediated antigen retrieval was performed in citrate buffer (pH6, epitope retrieval solution ) for 20 mins. The tissue section was blocked with 10% goat serum. The tissue section was then incubated with 1μg/mL rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) overnight at 4°C. DyLight 488 Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (BA1127) was used as secondary antibody at 1:100 dilution and incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C. The section was counterstained with DAPI. Visualize using a fluorescence microscope and filter sets appropriate for the label used.
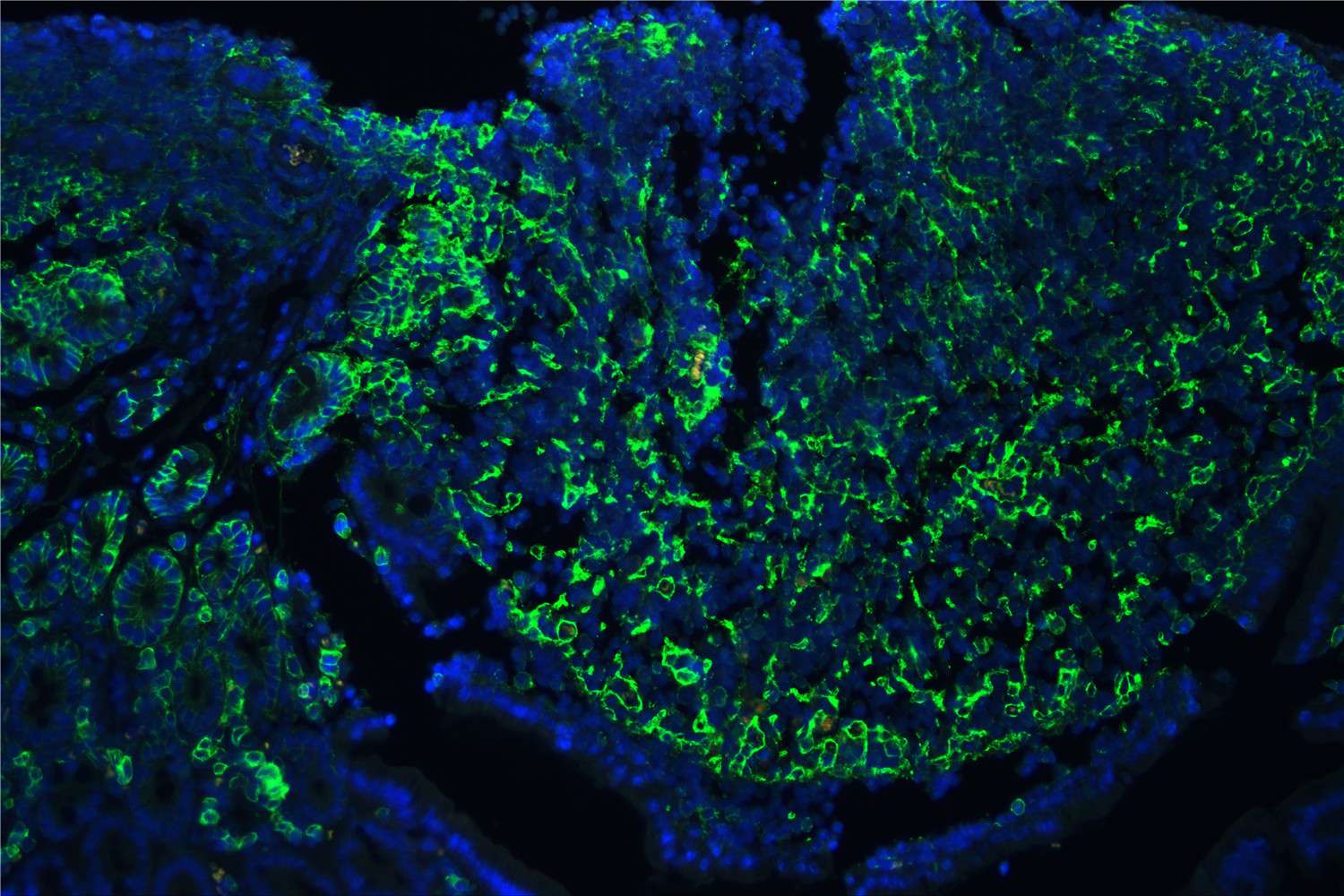
Figure 7. IF analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052)CD44 was detected in paraffin-embedded section of mouse lymphaden tissues. Heat mediated antigen retrieval was performed in citrate buffer (pH6, epitope retrieval solution ) for 20 mins. The tissue section was blocked with 10% goat serum. The tissue section was then incubated with 1μg/mL rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) overnight at 4°C. DyLight 488 Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (BA1127) was used as secondary antibody at 1:100 dilution and incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C. The section was counterstained with DAPI. Visualize using a fluorescence microscope and filter sets appropriate for the label used.
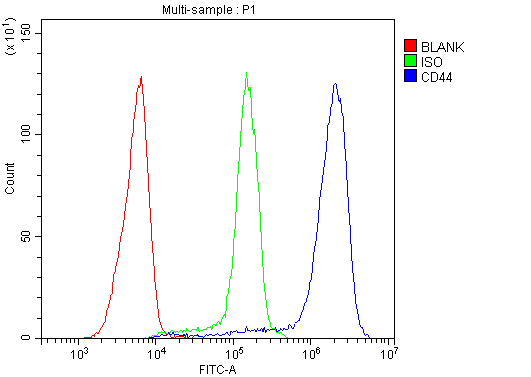
Figure 8. Flow Cytometry analysis of Jurkat cells using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
Overlay histogram showing Jurkat cells stained with A00052 (Blue line). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with permeabilization buffer. The cells were blocked with 10% normal goat serum. And then incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at 1:100 dilution for 30 min at 20°C. DyLight®488 conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (BA1127) was used as secondary antibody at 1:100 dilution for 30 minutes at 20°C. Isotype control antibody (Green line) was rabbit IgG at 1:100 dilution used under the same conditions. Unlabelled sample without incubation with primary antibody and secondary antibody (Red line) was used as a blank control.

Figure 1. Western blot analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052). The sample well of each lane was loaded with 30 ug of sample under reducing conditions.
Lane 1: human U251 whole cell lysates,
Lane 2: rat lung tissue lysates,
Lane 3: rat small intestine tissue lysates,
Lane 4: mouse lung tissue lysates.
After electrophoresis, proteins were transferred to a membrane. Then the membrane was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 antigen affinity purified polyclonal antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:1000 and probed with a goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP secondary antibody (Catalog # BA1054). The signal is developed using ECL Plus Western Blotting Substrate (Catalog # AR1197). A specific band was detected for CD44 at approximately 82 kDa. The expected band size for CD44 is at 82 kDa.

Figure 2. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of human colon cancer tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.

Figure 3. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of human placenta tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.

Figure 4. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of mouse kidney tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.

Figure 5. IHC analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
CD44 was detected in a paraffin-embedded section of rat kidney tissue. Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG was used as secondary antibody. The tissue section was incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at a dilution of 1:200 and developed using Strepavidin-Biotin-Complex (SABC) (Catalog # SA1022) with DAB (Catalog # AR1022) as the chromogen.

Figure 6. IF analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052)CD44 was detected in paraffin-embedded section of mouse lymphaden tissues. Heat mediated antigen retrieval was performed in citrate buffer (pH6, epitope retrieval solution ) for 20 mins. The tissue section was blocked with 10% goat serum. The tissue section was then incubated with 1μg/mL rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) overnight at 4°C. DyLight 488 Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (BA1127) was used as secondary antibody at 1:100 dilution and incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C. The section was counterstained with DAPI. Visualize using a fluorescence microscope and filter sets appropriate for the label used.

Figure 7. IF analysis of CD44 using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052)CD44 was detected in paraffin-embedded section of mouse lymphaden tissues. Heat mediated antigen retrieval was performed in citrate buffer (pH6, epitope retrieval solution ) for 20 mins. The tissue section was blocked with 10% goat serum. The tissue section was then incubated with 1μg/mL rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) overnight at 4°C. DyLight 488 Conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (BA1127) was used as secondary antibody at 1:100 dilution and incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C. The section was counterstained with DAPI. Visualize using a fluorescence microscope and filter sets appropriate for the label used.

Figure 8. Flow Cytometry analysis of Jurkat cells using anti-CD44 antibody (A00052).
Overlay histogram showing Jurkat cells stained with A00052 (Blue line). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with permeabilization buffer. The cells were blocked with 10% normal goat serum. And then incubated with rabbit anti-CD44 Antibody (A00052) at 1:100 dilution for 30 min at 20°C. DyLight®488 conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (BA1127) was used as secondary antibody at 1:100 dilution for 30 minutes at 20°C. Isotype control antibody (Green line) was rabbit IgG at 1:100 dilution used under the same conditions. Unlabelled sample without incubation with primary antibody and secondary antibody (Red line) was used as a blank control.









